An engine is a lump of metal which makes the vehicles go zoom. Major
types of engines are petrol and diesel. The engines required to run
petrol and diesel are different because petrol and diesel are different
types of fuel. Petrol is a highly volatile fuel and gets ignited very
easily whereas diesel is comparatively heavy and dirtier fuel. We would
be talking about 4 stroke engines only, the ones used in cars.
People who know me must be wondering why am I writing this article, i being a computer engineer. Hmmm, because, i am supposed to buy a car now and have been doing some research on them. The first question I came upon was whether a petrol or a diesel car. And, all i want to do is to share all that i have learned with you people. I am still unable to decide whether i should go for ford fiesta diesel or ford fiesta petrol, the petrol verson being a lot cheaper than the diesel version.
Lets start with what does a 4 stroke engine mean. It means that the engine has 4 strokes - inlet, compression, expansion and exhaust. Lets see stroke by stroke how both engines work
Petrol Engine

Diesel Engine
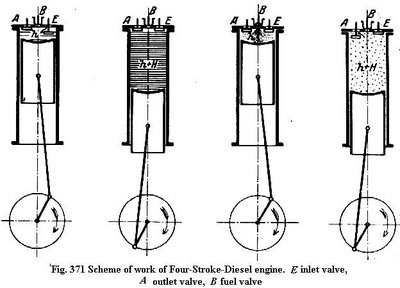
Inlet stroke
> In petrol engines the mixture of air and petrol is drawn in by the falling piston
> In diesel engines only air is drawn in by the falling piston
Compression stroke
> In petrol engine, the mixture is compressed upto about 1/8th to 1/12th of its original size.
> In diesel engine, only air is compressed upto about 1/14th to 1/25th of its original size.
Expansion stroke
> In petrol engine, the air and fuel mixture is ignited using a spark plug and burns expanding and forcing the piston down.
> In diesel engine, fuel is injected at a high pressure into the hot, compressed air in the cylinder, causing it to burn and force the piston down. No spark is required.
Exhause stroke
> In both petrol and diesel engines, the burned mixture of air and fuel is pushed out of the cylinder by the rising piston.
A diesel engine is also known as a "compression ignition" engine. Since the air is compressed to very high pressure raising its temperature and then diesel is injected in a very fine spray which causes the diesel to ignite and explode. Whereas a petrol engine is known as a "spark ignition" engine. Since a spark plug is required to ignite the mixture of petrol and air in the combustion chamber.
Diesel engine
Petrol engine

Lets also note down more differences of the same
Even after writing all this, i am still undecided where to go. Should i risk taking a diesel engine hoping that the maintenance costs would be bearable. Well, lets c what happens...
People who know me must be wondering why am I writing this article, i being a computer engineer. Hmmm, because, i am supposed to buy a car now and have been doing some research on them. The first question I came upon was whether a petrol or a diesel car. And, all i want to do is to share all that i have learned with you people. I am still unable to decide whether i should go for ford fiesta diesel or ford fiesta petrol, the petrol verson being a lot cheaper than the diesel version.
Lets start with what does a 4 stroke engine mean. It means that the engine has 4 strokes - inlet, compression, expansion and exhaust. Lets see stroke by stroke how both engines work
Petrol Engine

Diesel Engine

Inlet stroke
> In petrol engines the mixture of air and petrol is drawn in by the falling piston
> In diesel engines only air is drawn in by the falling piston
Compression stroke
> In petrol engine, the mixture is compressed upto about 1/8th to 1/12th of its original size.
> In diesel engine, only air is compressed upto about 1/14th to 1/25th of its original size.
Expansion stroke
> In petrol engine, the air and fuel mixture is ignited using a spark plug and burns expanding and forcing the piston down.
> In diesel engine, fuel is injected at a high pressure into the hot, compressed air in the cylinder, causing it to burn and force the piston down. No spark is required.
Exhause stroke
> In both petrol and diesel engines, the burned mixture of air and fuel is pushed out of the cylinder by the rising piston.
A diesel engine is also known as a "compression ignition" engine. Since the air is compressed to very high pressure raising its temperature and then diesel is injected in a very fine spray which causes the diesel to ignite and explode. Whereas a petrol engine is known as a "spark ignition" engine. Since a spark plug is required to ignite the mixture of petrol and air in the combustion chamber.
Diesel engine

Petrol engine

Lets also note down more differences of the same
- A diesel engine is more easily turbocharged than a petrol engine. A petrol engine cannot be easily turbocharged due to the fact that if the compression ratio and the pressure in the cylinder is to high during the inlet stroke, the mixture starts to burn to soon, while the piston is on its way up. The diesel engine has no fuel in the cylinder, thus letting the turbocharger suck as much air as it can without creating any problems. (A turbo charger is a simple air compressor which compresses air in the combustion chamber for burning). Some diesel engines also have an intercooler which helps in blowing cold and oxygen rich air in the combustion chamber.
- Electronic engine management not necessary in diesel engines. Some modern diesel engines are gaining electronically controlled injection pumps, but the vast majority of them out there have purely mechanical pumps. In fact no electricity is required to make a diesel engine run, except for a simple fuel cut off solenoid so that you can switch the thing off! If your alternator stops working, then you’re gonna get home in a diesel. This also means that a diesel engine does not have any ignition breakers, ignition coils, distributors and ignition wires to go bad. So a diesel engine should start no matter if it is dry or rainy or wet.
- Petrol destroys lubrication and burns the engine whereas diesel doesnt. So a diesel engine would last longer than a petrol engine.
- Petrol engines are lighter than diesel engines.
- Diesel engines have higher torque than petrol engines. What does this mean? Well, this means that a diesel engine would pull heavy loads easily than a petrol engine. Though the pickup of a petrol engine would be much more than that of a diesel engine, the diesel engine would be steady and carry heavier loads to longer distances.
- Diesel engines have better fuel efficiency as compared to petrol due to the fact that they have higher compression ratio.
- Diesel engines dont need an ignition system, which reduces their complexity. But they are more noisy and may require frequent maintenance as compared to petrol engines. Also they are more durable.
- Diesel engines may also need glow plugs in extreme cold conditions which heat up the cylinder so that a cold engine can start easily.
- And now the most important part, fuel economy. Diesel wins in both ways. Diesel engines give better mileage than petrol engines and In india diesel is much cheaper than petrol. So running on diesel would make you go farther at a lower cost than running on petrol.
Even after writing all this, i am still undecided where to go. Should i risk taking a diesel engine hoping that the maintenance costs would be bearable. Well, lets c what happens...


.png)